Dermatology
Removal of papillomas
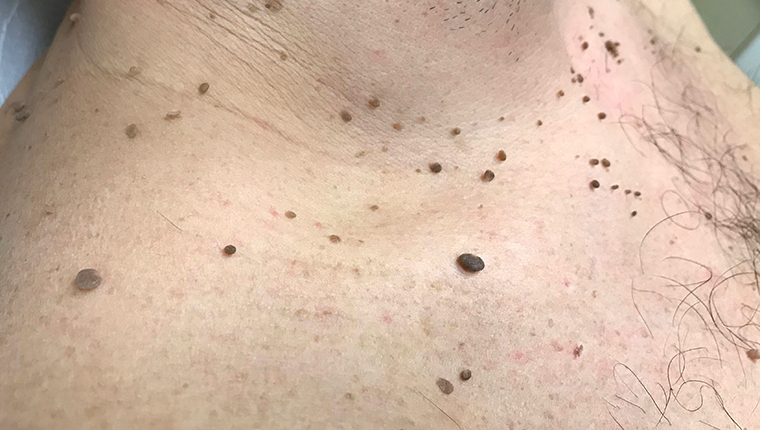
Papillomas, also known as moles, also known as moles, are small, round, benign skin tumors. Usually they are of the same color as that of the skin, while they may be pinkish, brown or even dark-colored. In the latter case, papillomas resemble common nevi (moles). They are due to HPV viruses, i.e. viruses that cause warts and genital warts only that they are not equally contagious.
Symptoms
Papillomas are usually asymptomatic and are particularly common in individuals after the age of 25-30. But when they become too large or proliferated they can cause itching, burning or even bleeding in case of self-injury. They usually appear in warm and wet areas of the body, where the skin creates folds and favors the development of HPV. Such areas are the neck, the face and particularly the eyelids, armpits, chest and groin.
Although papillomas can occur in all people, their occurrence is favored by the following predisposing factors: Body Weight (overweight or obese people), pregnancy, endocrinopathies, skin injuries, co-presence of warts or genital, heredity.
Diagnosis of papillomas should be made exclusively by a dermatologist following clinical examination, with the exception of cases where a biopsy is required. In any case, their removal is imperative, both for medical and cosmetic reasons.
Treatment
The main methods of removing papillomas are surgical resection, electroporation, plasma mediated electrosurgery, radio frequency ablation, CO2 laser removal, and cryotherapy.
- Surgical removal. It is indicated in major lesions or moluscum contagiosum. It is usually performed by surface resection without sutures; it is safe, fast and does not leave any scars.
- Laser CO2 removal. It is one of the most state-of-the art and effective therapies. It immediately offers complete healing without signs and scarring, while patients immediately resume their daily activities.
- Removal by electrosurgery. This technique damages or removes lesions using electrosurgery or by using a more recent plasma mediated electrosurgery. This method has excellent results but is relatively more painful than the previous ones and the use of local anesthesia is required. The burns caused may take several days to heal, and there is a risk of scarring.
- Removal of papilla by cryotherapy. This technique uses liquid nitrogen, either by direct spraying or using a special stylet. The papilla is frozen, then shrinks and falls off. It is a safe method but may need to be repeated more than once, and it can cause burns in the adjacent areas and scarring in rare cases.
- Papilla removal by radiofrequency. More recent technique in which, by means of a special radiofrequency generating device, using a special tip like a needle, the papules are cut off without necessitating anesthesia with excellent results. The method is painless, with excellent results and safe, and there is no risk of post-operative scarring or injuries.
A. No, the virus causing the warts is different
A. Yes, following your dermatologist’s postoperative instructions, you can return to your work the same day.
A. With the LP technique, pain is minimized, but we usually recommend to have applied some local anesthetic cream half an hour before the procedure to minimize sensitivity.
A. It is possible for new ones to develop but not the same ones.